데이터를 생성하거나 수정할 때, 누가, 언제 해당 작업을 했는지 알기 위해 보통 아래와 같은 필드를 공통으로 각 테이블에 포함 시켜 테이블을 설계한다.
createdAt(생성일자)modifiedAt(수정일자)createdBy(생성자)modifiedBy(수정자)
생성 일자와 생성자는 테이블에 신규 레코드(row)가 생길 때마다 입력되어야 하고 수정 일자와 수정자는 특정 row 가 업데이트될 때마다 반영되어야 한다.
그냥 구현한다면?
가장 간단한 방법으로는 생성자 또는 setter 메소드를 활용하여 직접 값을 설정하면 된다.
@Table(name = members)
@Entity
public class Member {
...
@Column
private Datetime createdAt;
@Column
private Datetime modifiedAt;
@Column
private String createdBy;
@Column
private String modifiedBy;
public Member(..., String requestedBy) {
...
this.createdAt = Datetime.now();
this.modifiedAt = Datetime.now();
this.createdBy = requestedBy;
this.modifiedBy = requestedBy;
}
public modify(..., String requestedBy) {
...
this.modifiedAt = Datetime.now();
this.modifiedBy = requestedBy;
}
}하지만 매번 이렇게 코드를 작성하는 것은 귀찮고 번거롭다. 엔티티가 많으면 하나하나 다 해줘야 하고.. 매번 파라미터로 requestedBy 를 전달하는 것도 여간 귀찮은게 아니다.
@EnableJpaAuditing
엔티티 객체가 생성이 되거나 변경이 되었을 때 @EnableJpaAuditing 어노테이션을 활용해서 자동으로 값을 등록할 수 있다. 어떻게 사용하는지 알아보도록 하자.
1. 의존성 관련 설정
@EnableJpaAuditing 어노테이션은 Spring Data 에서 제공하므로 아래처럼 의존성을 추가해주어야 한다.
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa'
}2. 생성일자, 생성자를 위한 공통 엔티티 생성
생성일자 와 생성자 를 관리하는 클래스로 BaseEntity 를 생성한다.
@MappedSuperclass // ... (1)
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener::class) // ... (2)
public abstract class BaseEntity {
@CreatedDate // ... (3)
@Column(updatable = false) // ... (4)
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
@CreatedBy
@Column(updatable = false)
private String createdBy;
}어노테이션 설명
- (1)
@MappedSuperclass: 공통 맵핑 정보가 필요할 때 사용하며 부모 클래스에서 선언하고 속성만 상속 받아서 사용하고 싶을 때 사용한다.BaseEntity를 상속받는 클래스는 모두createdAt,createdBy필드가 있어야 한다. - (2)
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener::class): JPA Entity 에 이벤트가 발생할 관련 코드를 실행한다. - (3)
@CreatedDate: 생성일자를 관리하는 필드에 현재 날짜를 주입하는 작업을 수행한다. - (4)
@Column(updatable = false): 생성일자, 생성자에 대한 필드이기 때문에 수정 불가하도록 설정한다.
3. 수정일자, 수정자를 위한 공통 엔티티 생성
수정일자와 수정자를 관리하는 클래스로 MutableBaseEntity 를 생성한다.
@MappedSuperclass
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener::class)
public abstract class MutableBaseEntity extends BaseEntity {
@LastModifiedDate
@Column(updatable = true)
private LocalDateTime modifiedAt;
@LastModifiedBy
@Column(updatable = true)
private String modifiedBy;
}4. 생성자, 수정자를 입력받기 위한 설계
생성 일자와 수정 일자의 경우, ZonedDateTime.now() 를 통해 현시각으로 쉽게 설정할 수 있는 반면, 생성자와 수정자의 경우에는 하드코딩된 값을 입력할게 아니라면 외부에서 주입을 받아서 AuditingEntityListener 가 입력할 수 있도록 해줘야 한다. 다양한 방법이 있을 수 있겠지만 여기서는 API 요청의 Header 에 포함시켜 생성자와 수정자를 지정해보려고 한다.
먼저 클래스 다이어그램을 그려보았다. 기능 구현을 위해서는 Web 계층, Domain 계층, 그리고 Persistence 계층으로 크게 3개의 계층이 필요하다.
- Web 계층: API 요청의 Header 를 참조해 생성자와 수정자에 값이 될 요청자 (requestedBy) 를 찾고, 이 값을 스프링 IoC 컨테이너 내 빈으로 등록된
ApplicationHolderImpl에 저장해둔다.- WebRequestInterceptor 와 WebMvcConfigurer 는 스프링에서 제공하는 인터페이스이다.
- Domain 계층: 각 Entity 에 존재하는
createdBy와modifiedBy에 대해 값 업데이트가 필요할 경우RequestedByAuditAware는 스프링 IoC 컨테이너를 참조해 요청자를 찾아 값을 주입한다. - Persistence 계층:
@EnableJpaAuditing어노테이션을 통해 Auditing 을 활성화 시키고 관련 속성 클래스로RequestedByAuditAware클래스를 참조한다.

위 클래스 다이어그램을 참조하여 아래 예시 상황을 이해해보자.
데이터를 수정하는 PUT API 요청이 들어왔고, API 헤더에는 requested-by 라는 값에 수정자 kdohyeon 으로 설정되어 전달되었다.
// API 헤더
{
"requested-by": "kdohyeon"
}요청이 들어오면 먼저 수행해야 할 작업은 스프링 IoC 컨테이너에 해당 값을 저장해두는 것이다. 이걸 하기 위해서는 WebRequestInterceptor 를 상속받는 RequestedByInterceptor 를 구현하면 된다. 웹 요청이 들어왔을 때 InterceptorRepository 의 인터셉터들이 실행되게 되는데 그 중 하나로 RequestedByInterceptor 를 추가하면 된다.
RequestedByInterceptor.java
- 먼저
RequestedByInterceptor를 살펴보면, WebRequest 에 포함된 헤더 정보를 꺼내requested-by속성으로RequestedBy객체를 만들어AuthenticationHolder에 추가한다. 만약requested-by가 없으면null값이 들어간다. 이제 AuthenticationHolder 에서는 헤더 정보에 있던requested-by를 언제든 꺼내 확인해볼 수 있다.
@Component
public class RequestedByInterceptor implements WebRequestInterceptor {
public static final String REQUESTED_BY_HEADER = "requested-by";
private final AuthenticationHolder authenticationHolder;
public RequestedByInterceptor(AuthenticationHolder authenticationHolder) {
this.authenticationHolder = authenticationHolder;
}
@Override
public void preHandle(WebRequest request) {
String requestedBy = request.getHeader(REQUESTED_BY_HEADER);
RequestedBy requestUser = new RequestedBy(requestedBy);
authenticationHolder.setAuthentication(requestUser);
}
@Override
public void postHandle(WebRequest request, ModelMap model) {
...
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(WebRequest request, Exception ex) {
...
}
}RequestedByMvcConfigurer.java
- InterceptorRegistry 에 인터셉터
RequestedByInterceptor를 추가해준다.
@EnableWebMvc
@Configuration
public class RequestedByMvcConfigurer implements WebMvcConfigurer {
private final RequestedByInterceptor requestedByInterceptor;
public RequestedByMvcConfigurer(RequestedByInterceptor requestedByInterceptor) {
this.requestedByInterceptor = requestedByInterceptor;
}
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addWebRequestInterceptor(requestedByInterceptor);
}
}RequestedBy.java
- 요청자 정보를 저장하는 자바 객체로 Authentication 을 상속받고 있다.
- 만약 이름 말고도 email, mobile 등 기타 정보를 헤더를 통해 받는다면 이 클래스에 필드를 추가하여 관리할 수 있다.
@Getter
public class RequestedBy implements Authentication {
private final String requestedBy;
public RequestedBy(String requestedBy) {
this.requestedBy = requestedBy;
}
}Authentication.java
- 인증 정보에 대한 인터페이스로
RequestedBy가 상속받아 사용함
public interface Authentication {
String getRequestedBy();
}AuthenticationHolder.java
- 헤더에서 받은 인증 정보를 포함할 수 있는 인터페이스
public interface AuthenticationHolder {
Optional<Authentication> getAuthentication();
void setAuthentication(Authentication authentication);
}AuthenticationHolderImpl.java
- AuthenticationHolder 와 RequestedByProvider 를 구현한 구현체
@Component
public class AuthenticationHolderImpl implements AuthenticationHolder, RequestedByProvider {
private Authentication authentication;
@Override
public Optional<Authentication> getAuthentication() {
return Optional.ofNullable(this.authentication);
}
@Override
public void setAuthentication(Authentication authentication) {
this.authentication = authentication;
}
@Override
public Optional<String> getRequestedBy() {
return getAuthentication()
.map(Authentication::getRequestedBy);
}
}RequestedByProvider.java
public interface RequestedByProvider {
Optional<String> getRequestedBy();
}createdBy 또는 modifiedBy 에 값이 Auditing 되어야 하는 경우를 감지하려면 @EnableJpaAuditing 어노테이션을 부여해줘야 한다. 이 이노테이션으로 createdBy, modifiedBy 에 값을 주입할 때는 auditorAwareRef 속성을 참고하고, createdAt, modifiedAt 에 시간 값을 정의할 때에는 dateTimeProviderRef 속성을 참고해서 값을 설정할 수 있다.
JpaAuditConfig.java
@EnableJpaAuditing(
auditorAwareRef = "requestedByAuditorAware",
dateTimeProviderRef = "requestedByAuditorAware"
)
@Configuration
public class JpaAuditConfig {
...
}RequestedByAuditorAware.java
- 스프링 IoC 컨테이너에서
RequestedByProvider를 꺼내requestedBy값을 가져온다. - 만약 값이 존재하지 않을 경우 (=헤더에서
requested-by값이 없는 경우)에는 기본값system을 활용한다.
@Component
public class RequestedByAuditorAware implements AuditorAware<String> {
private static final String SYSTEM = "system";
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public RequestedByAuditorAware(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Override
public Optional<String> getCurrentAuditor() {
try {
return Optional.of(applicationContext.getBean(RequestedByProvider.class))
.flatMap(RequestedByProvider::getRequestedBy);
} catch (Exception e) {
return Optional.of(SYSTEM); // 입력되지 않은 경우에는 기본값 "system" 으로 사용
}
}
}5. JPA Entity 적용
BaseEntity 와 MutableBaseEntity 클래스를 생성한 뒤, 다시 Member 엔티티로 돌아가서,
MutableBaseEntity 를 상속받았기 때문에 createdAt, createdBy, modifiedAt, modifiedBy 과 관련된 코드는 삭제해도 된다.
@Table(name = members)
@Entity
public class Member extends MutableBaseEntity {
...
}Issues
@EnableJpaAuditing 어노테이션을 적용하면서 해결해나갔던 이슈들을 정리한다.
Issue 1. dateTime format error
datetime 포맷이 맞지 않다면서 엔티티 저장이 제대로 되지 않았는데, 아래 글을 참고하여 해결을 했다.
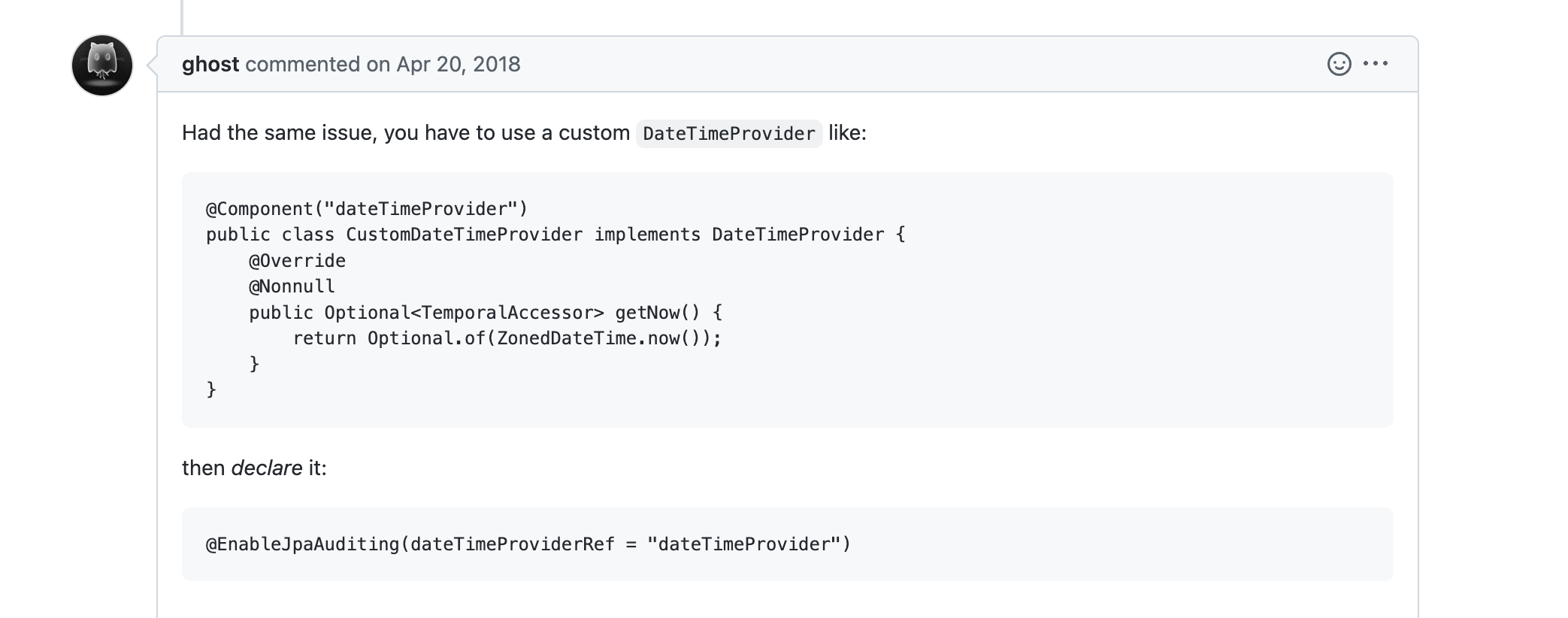
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/issues/10743
@EnableJpaAuditing 에 dateTimeProviderRef 도 있고 auditorAwareRef 라는 속성도 있다. 날짜와 관련된 속성은 dateTimeProviderRef 로 설정할 수 있으니 필요하면 꼭 넣어야 한다.
Issue 2. ZonedDateTime 숫자값으로 표현
아래 그림처럼 modifiedAt 이 숫자값으로 표현이 된다.
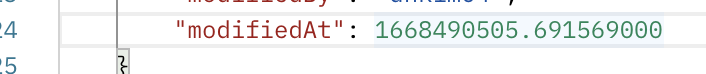
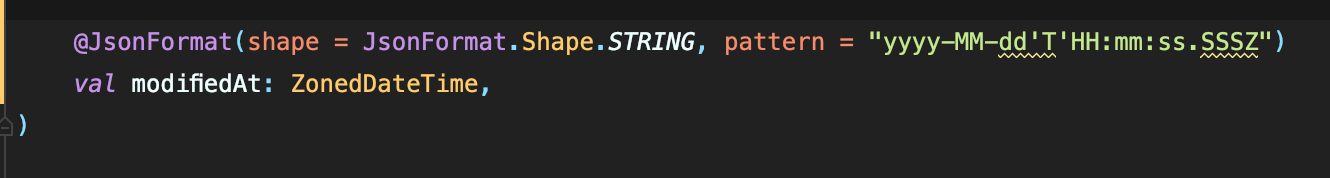
날짜로 표현되어야 하는데... 해결하는 방법은 @JsonFormat 을 사용하면 된다.
Reference
'JPA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JPA] Spring 에서 JPA 사용하기 (0) | 2023.02.11 |
|---|---|
| [JPA] @ManyToOne, @OneToMany 를 활용하기 (0) | 2023.02.10 |
| [JPA] @OrderBy (0) | 2023.02.03 |



댓글